Role of Simulation in Healthcare
- Home
- College of Health and Pharmacy
- Simulation Education Center
- About Simulation
- Role of Simulation in Healthcare
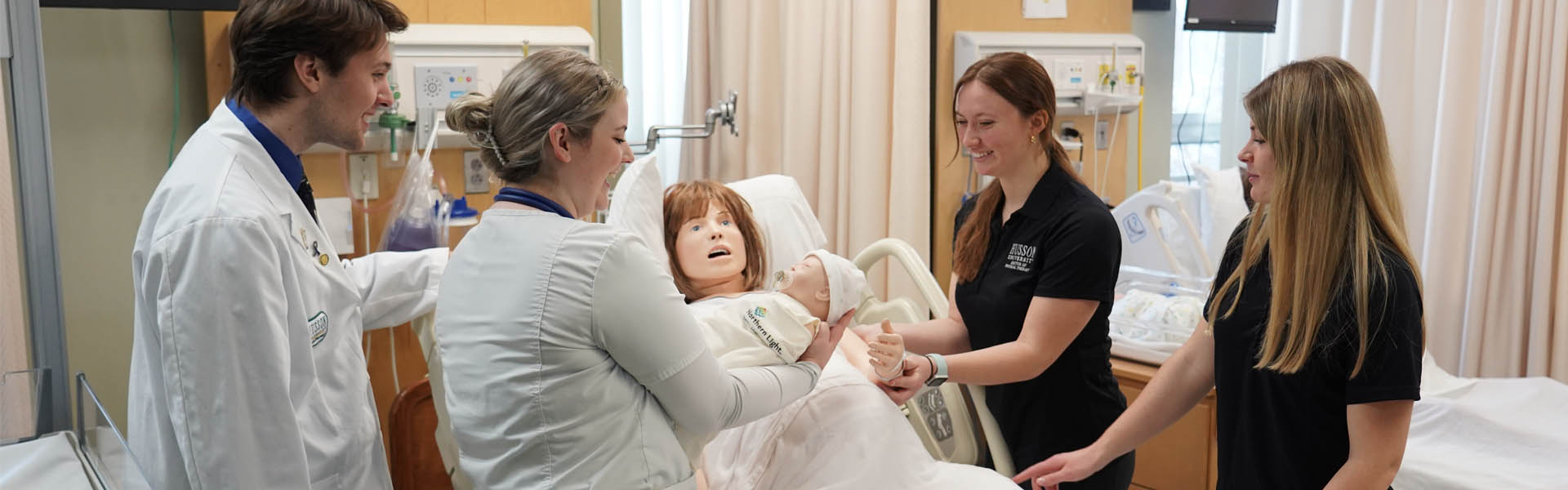
Simulation education is a key bridge between classroom learning and clinical experience. It offers a safe environment for healthcare providers to perfect their skills without exposing patients to any risks. For example, novices and patients can learn how to administer injections using a real needle and syringe on an orange. Advanced simulations utilize computerized mannequins that can replicate dozens of human functions with remarkable accuracy. During simulations, healthcare personnel are shielded from unique hazards like contaminated needles, blades, electrical equipment, etc., that they might encounter in actual healthcare settings. Systems integration in healthcare involves using simulation-based processes to evaluate performance, ensure patient safety, and test new procedures before implementation or for disaster response training.
Simulation-based research aims to understand events and test medical devices under different simulated conditions. Computer-generated data patterns represent populations and tests, and simulations can be combined to analyze issues from various angles. Research is necessary to validate the simulation tool.
Systems integration in healthcare refers to the integration of simulation-based training and assessment mechanisms. This approach can improve patient safety, enhance objectivity and fairness in evaluations, and test new procedures before implementation. Simulation-based evaluations can effectively evaluate organizational processes and individual team performance, including disaster response training.
